Paclitaxel is recommended as a first-line chemotherapeutic agent against ovarian cancer, but drug resistance becomes a major limitation of its success clinically. The key molecule or mechanism associated with paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer still remains unclear.
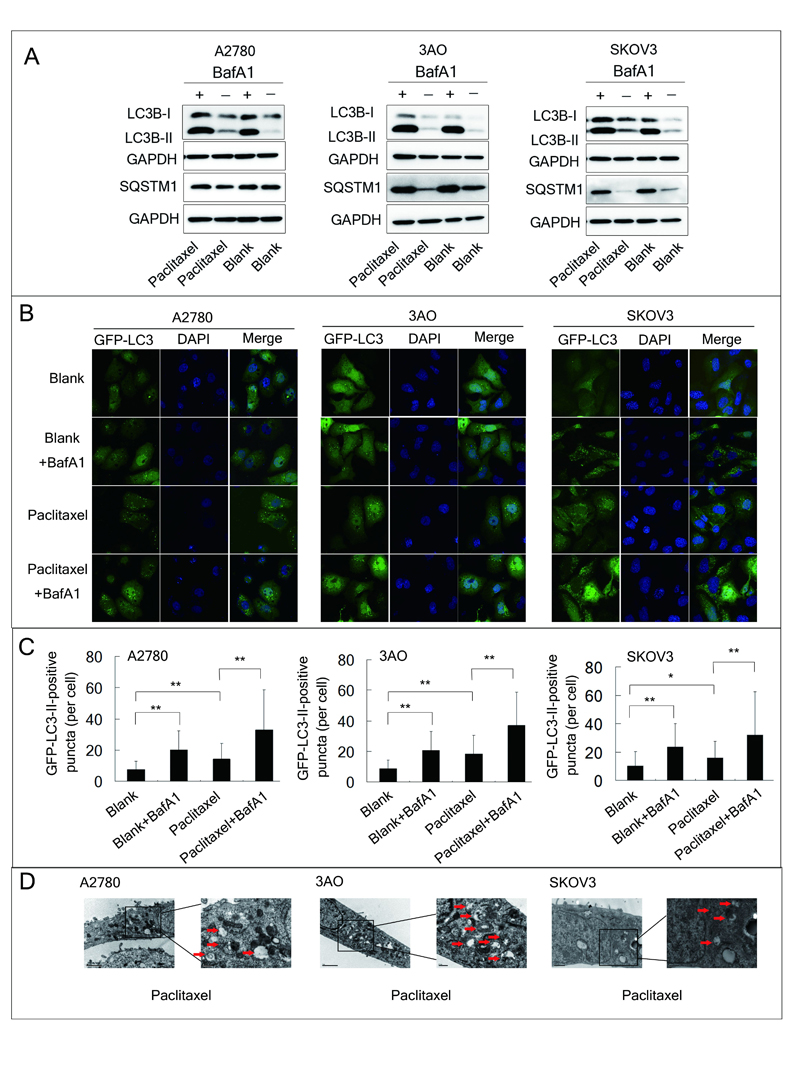
In this study, Professor Xing Xie’s group showed that TXNDC17 screened from 356 differentially expressed proteins by LC-MS/MS label-free quantitative proteomics was more highly expressed in paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells and tissues, and the high expression of TXNDC17 was associated with poorer prognostic factors and exhibited shortened survival in 157 ovarian cancer patients. Moreover, paclitaxel exposure induced upregulation of TXNDC17 and BECN1 expression, increase of autophagosome formation, and autophagic flux that conferred cytoprotection for ovarian cancer cells from paclitaxel. TXNDC17 inhibition by siRNA or enforced overexpression by a pcDNA3.1(C)-TXNDC17 plasmid correspondingly decreased or increased the autophagy response and paclitaxel resistance. Additionally, the downregulation of BECN1 by siRNA attenuated the activation of autophagy and cytoprotection from paclitaxel induced by TXNDC17 overexpression in ovarian cancer cells. Thus, our findings suggest that TXNDC17, through participation of BECN1, induces autophagy and consequently results in paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. TXNDC17 may be a potential predictor or target in ovarian cancer therapeutics.
These results were published in Autophagy. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.81372789), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LZ14h760001), National High Technology Research and Development Program 863 (Grant No.2012AA02A507), Zhejiang Provincial Medicine and Health Technology Plan (Grant No. 2012RCA038).